Introduction
Geogrids are essential in modern construction projects, serving as reinforcement for soil and other granular materials. Among the most commonly used types of geogrids are polyester geogrid and fiberglass geogrid. While they share some similarities, their differences make them suitable for specific applications. In this article, we’ll delve into their unique characteristics, applications, and benefits to help you make informed decisions for your projects.
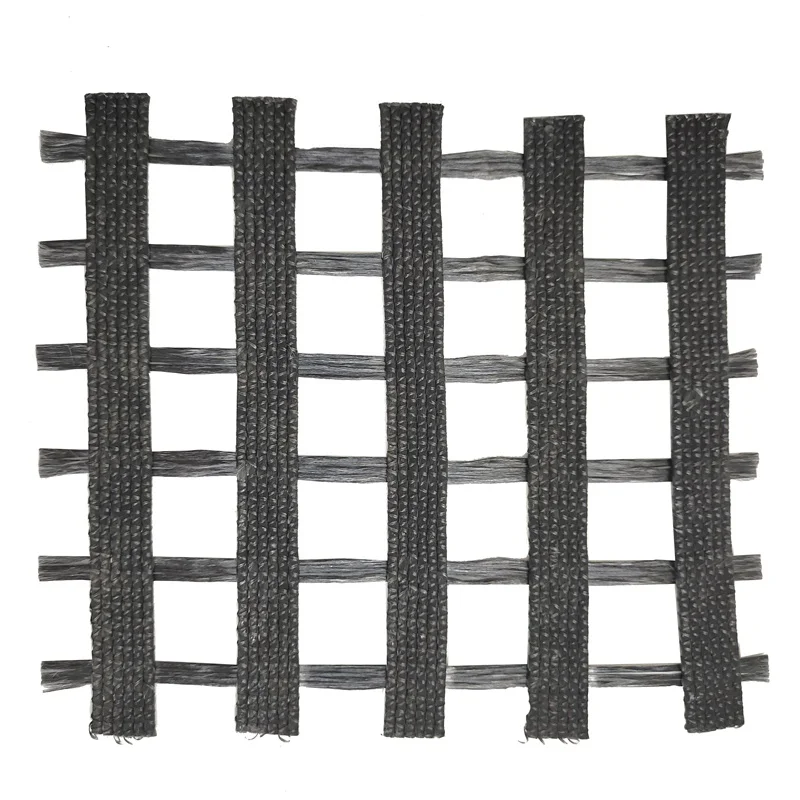

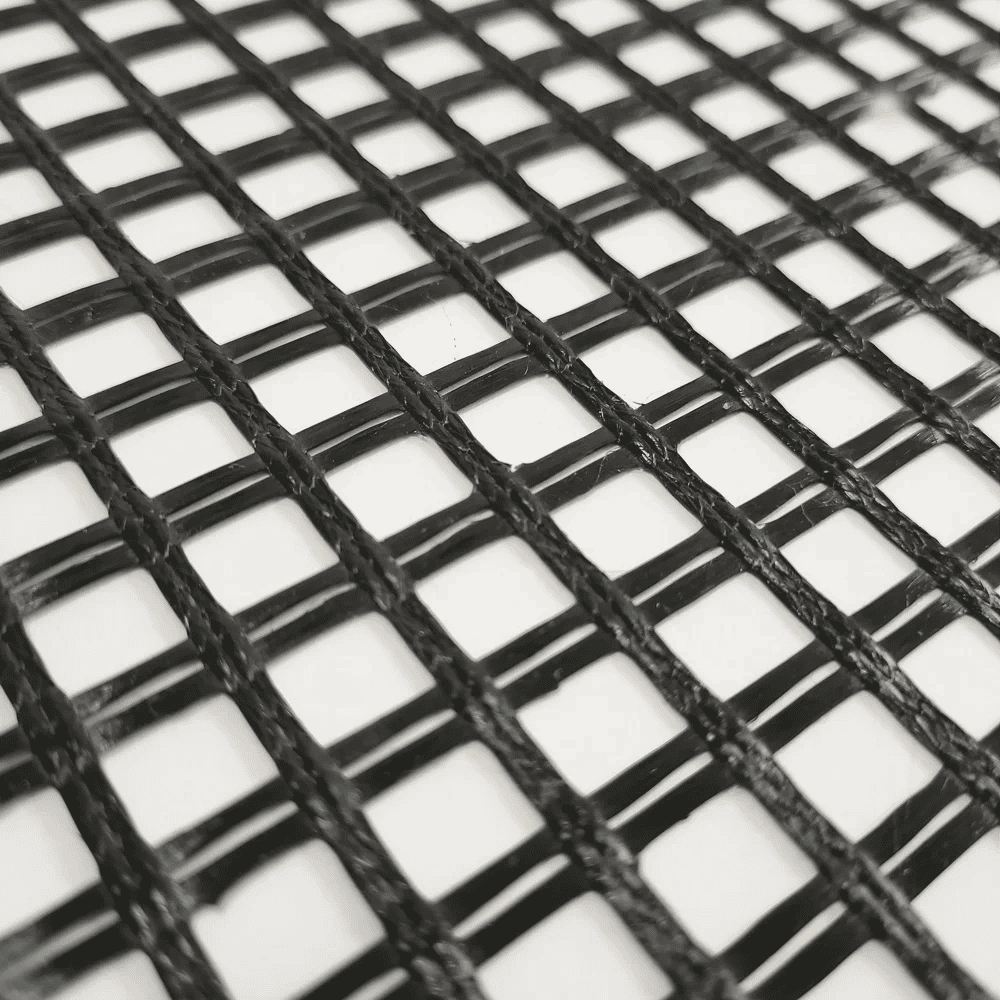
What Are Geogrids?
Geogrids are geosynthetic materials designed for soil stabilization and reinforcement. They consist of a grid-like structure that provides mechanical interlocking, distributing loads over a larger area and enhancing structural integrity. Geogrids are widely used in road construction, retaining walls, embankments, and other infrastructure projects. They are preferred for their ability to reduce maintenance costs and improve the lifespan of structures by preventing deformation and cracking.
Polyester Geogrid: Characteristics and Applications
Characteristics of Polyester Geogrid
Material Composition: Made from high-tenacity polyester fibers, often coated with polymer or PVC for added durability.
Tensile Strength: Known for its high tensile strength, especially in environments with low or no chemical exposure.
Flexibility: Offers excellent flexibility, allowing it to adapt to varying ground conditions.
Chemical Resistance: Limited resistance to aggressive alkaline or acidic conditions unless specially treated.
Cost-Effectiveness: Often more affordable than fiberglass geogrid, making it a popular choice for large-scale projects.
Applications of Polyester Geogrid
- Road Construction: Used to reinforce subgrades and prevent rutting, especially in soft soil conditions.
- Retaining Walls: Provides stability by distributing loads evenly, reducing wall deformation.
- Slope Stabilization: Effective in preventing landslides and erosion in slopes and embankments.
- Railways: Reinforces railway foundations by reducing settlement and enhancing stability.
- Industrial Yards: Useful in areas where heavy loads and machinery are present, ensuring ground stability.
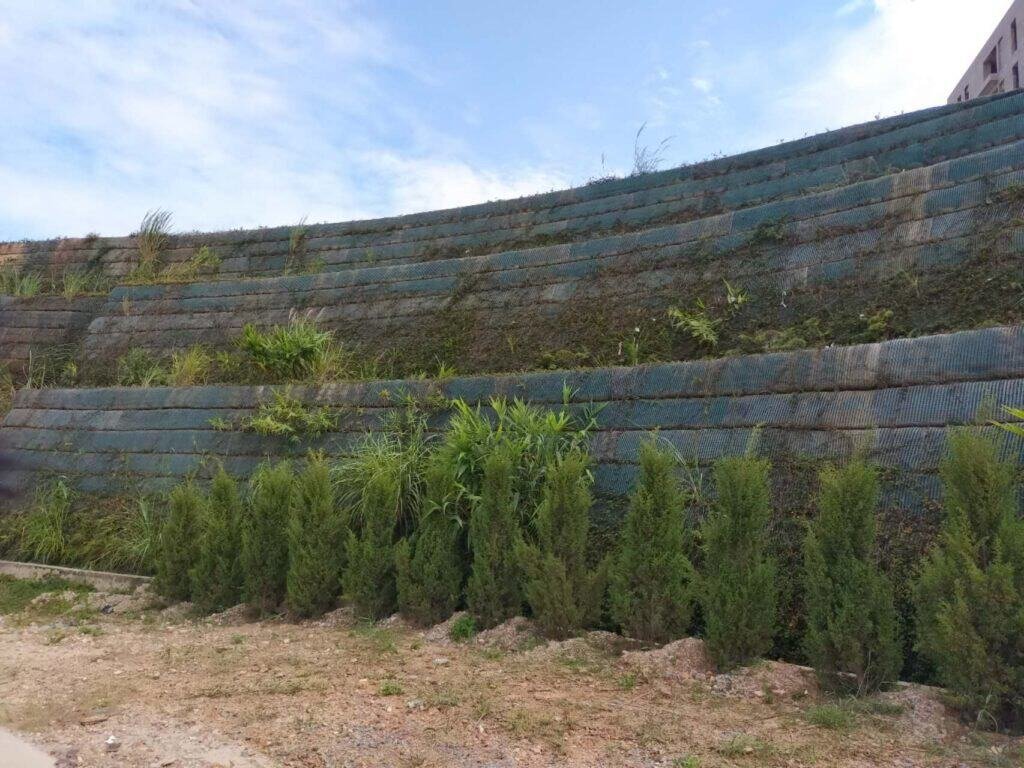

Fiberglass Geogrid: Characteristics and Applications
Characteristics of Fiberglass Geogrid
Material Composition: Constructed from fiberglass strands with a polymer coating for added durability and resistance.
Tensile Strength: Offers exceptional tensile strength, particularly at low elongation rates.
Chemical Resistance: Excellent resistance to chemical degradation, particularly in alkaline environments.
Thermal Stability: High resistance to temperature variations, making it suitable for hot asphalt overlays.
Applications of Fiberglass Geogrid
Asphalt Pavements: Commonly used in asphalt overlays to reduce cracking and extend the lifespan of roads.
Bridge Deck Reinforcement: Enhances the durability of bridge decks by mitigating reflective cracking.
Parking Lots: Used to reinforce asphalt surfaces in commercial and industrial parking areas.
Runways: Provides stability and reduces maintenance costs for airport runways subjected to heavy loads.
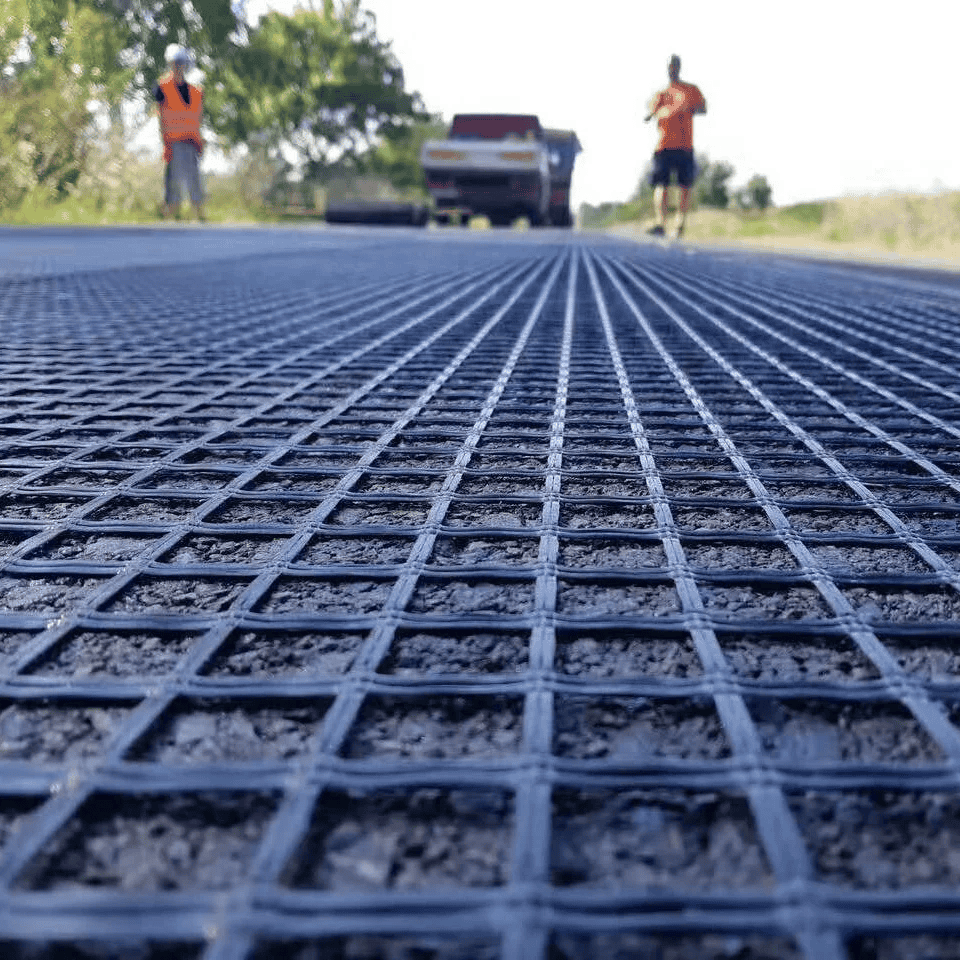

Key Differences Polyester Geogrid and Fiberglass Geogrid
| Aspect | Polyester Geogrid | Fiberglass Geogrid |
| Material | High-tenacity polyester fibers | Fiberglass strands with polymer coating |
| Tensile Strength | High, adaptable to soft soils | Very high, suitable for asphalt overlays |
| Chemical Resistance | Limited to moderate | Excellent, especially in alkaline settings |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, ideal for uneven terrain | Rigid, suitable for flat surfaces |
| Temperature Resistance | Moderate | Excellent, handles high temperatures well |
| Common Uses | Soil stabilization, retaining walls | Asphalt overlays, bridge decks |
Benefits of Choosing the Right Geogrid
Selecting the right geogrid is crucial for achieving optimal results in construction projects. Here are the primary benefits of using polyester and fiberglass geogrids:
- Enhanced Structural Integrity: Both types improve the load-bearing capacity of soil and asphalt layers.
- Cost Savings: Reduce maintenance costs by preventing deformation and cracking.
- Environmental Impact: Minimize the use of raw materials like asphalt and concrete by extending the lifespan of structures.
Conclusion
Both polyester and fiberglass geogrids offer unique advantages tailored to specific applications. Polyester geogrids excel in soil stabilization and slope reinforcement, while fiberglass geogrids are ideal for asphalt overlays and chemically aggressive environments. By understanding their differences, you can choose the right solution for your project’s needs, ensuring long-term performance and cost-efficiency.
For more insights and high-quality geogrids, visit our website today!





